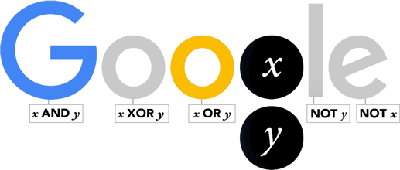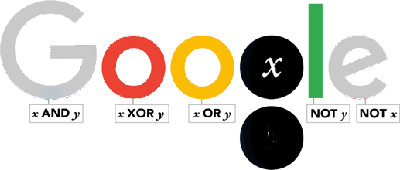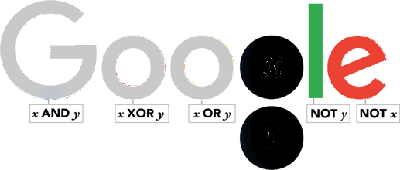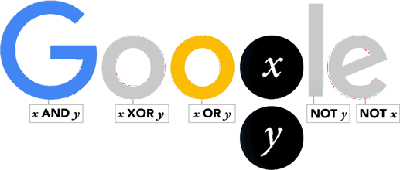| George Boole, Boolean Logic and Computing |
| Sunday, 02 November 2025 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Today we celebrate the 210th anniversary of the birth of George Boole who today we credit with being the "forefather of the digital age", thanks to his creation of a method of formal logic in which statements are defined as being either true or false. George Boole was born in Lincoln, England, the son of a struggling shoemaker. Forced to leave school at 16, he never attended a university but instead taught himself languages, natural philosophy and mathematics. He began his career as a schoolteacher, writing articles on mathematics in his spare time. These investigations led to the book Mathematical Analysis of Logic. Queen's University at Cork, Ireland, recognized Boole's contributions and offered him the chair of mathematics in 1848. This opportunity allowed Boole to extend his studies and produce his most significant work An Investigation of the Laws of Thought, which sets out his method of expressing the workings of the human mind in symbolic form. He died at the age of 49 in 1864 and his work might never have had an impact on computer science without Claude Shannon, who 70 years later recognised the relevance for engineering of Boole’s symbolic logic. As a result, Boole’s thinking has become the practical foundation of digital circuit design and the theoretical grounding of the the digital age. Hence is now acknowleged as its "forefather". To celebrate the bicentenary of his birth, November 2, 2015, Google produced this Doodle which is a self-contained lesson of Boolean logic in action:
Notice that under each of the letters is a logical expression. Start with the one under the G which reads x AND y. This is a simple Boolean expression and it is only true is x is true and y is true. Now look at the two circles where the Google g should be. Notice that it is cycling though showing all combinations of x and y. When either letter is showing then it is taken as true in the evaluation of all of the Boolean expressions in the doodle. So when you see both x and y on display x is true and y is true and this means x AND y is true and so G has its usual blue color. The rule is x and y are true if they are on display. All of the Boolean expressions are evaluated using the current state of x and y and if true the letter above shows in the usual color - if false the letter shows as a grey. Now you should be able to see the pattern even if you are new to Boolean logic. For example, the first o only shows when x XOR y is true. The XOR logical operator is only true if exactly one of x or y is true. That is its "truth table" is:
You can find out about truth tables and the importance of Boolean logic in Introduction to Boolean Logic.
George Boole
Related ArticlesThe Greeks, George Boole and Prolog To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info <ASIN:1871962439>
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Last Updated ( Sunday, 02 November 2025 ) |