|
Page 4 of 6
Start a new Win Form .NET 8 project and place a button labeled "Get Disk Status" and two RichTextBoxes.
The Button's event handler first loads a list of drives and their status into the first RichTextBox:
ManagementObjectSearcher WMISearch =
new ManagementObjectSearcher(
"Select * from Win32_DiskDrive");
ManagementObjectCollection Drives =
WMISearch.Get();
richTextBox1.Text = "Drive\t\t\tStatus\n";
foreach (ManagementObject Drive in Drives)
{
richTextBox1.Text = richTextBox1.Text +
Drive.Properties["DeviceId"].
Value.ToString() + "\t";
richTextBox1.Text = richTextBox1.Text +
Drive.Properties["Status"].
Value.ToString() + "\n";
}
To get and decode the data returned by WMI we need another RichTextBox and some appropriate headings:
richTextBox2.Text =
"Unknw\tUnknw\tAttribute
\tStatus\tUnknw\tValue\
tWorst\tRaw\t\tUnknw\n";
Now to display each set of FailData we need a foreach loop:
foreach ( ManagementObject FailData in
FailDataSet )
{
The data is returned as an object type but we know it’s really a byte array and the simplest way of working with it is to retrieve it and cast it to a byte array:
Byte[] data = (Byte[])FailData.
Properties["VendorSpecific"].Value;
Finally we can add each attribute to the RichTextBox making use of the fact that each block of 12 bytes corresponds to an attribute:
for (int i = 0; i < data[0]-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 12; j++)
{
richTextBox2.Text = richTextBox2.Text
+ data[i*12+j] + "\t";
}
richTextBox2.Text = richTextBox2.Text + "\n";
}
If you now run the program you will see the raw SMART data displayed as a table. Your next task is to process it and build it into a useful reporting tool that will warn you if anything is going wrong.
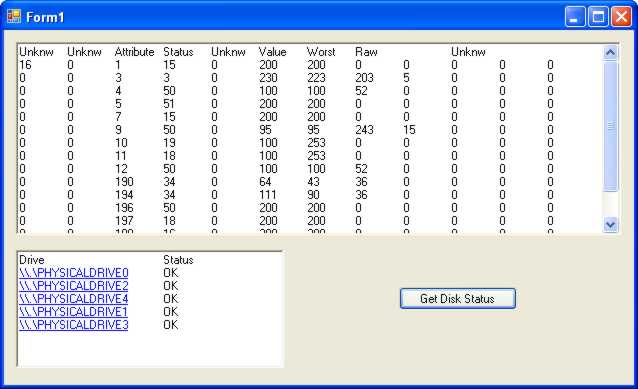
The raw SMART data
The complete program is:
namespace WinFormsApp1
{
using System.Management;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
richTextBox2.Text = "Unknw\tUnknw\tAttribute
\tStatus\tUnknw\tValue\tWorst
\tRaw\t\tUnknw\n";
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
ManagementObjectSearcher WMISearch =
new ManagementObjectSearcher(
"Select * from Win32_DiskDrive");
ManagementObjectCollection Drives =
WMISearch.Get();
richTextBox1.Text = "Drive\t\t\tStatus\n";
foreach (ManagementObject Drive in Drives)
{
richTextBox1.Text = richTextBox1.Text +
Drive.Properties["DeviceId"].
Value.ToString() + "\t";
richTextBox1.Text = richTextBox1.Text +
Drive.Properties["Status"].
Value.ToString() + "\n";
}
WMISearch.Scope = new ManagementScope(
@"\root\wmi");
WMISearch.Query = new ObjectQuery(
"Select * from
MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictData");
ManagementObjectCollection FailDataSet =
WMISearch.Get();
foreach (ManagementObject FailData
in FailDataSet)
{
Byte[] data = (Byte[])FailData.
Properties["VendorSpecific"].Value;
for (int i = 0; i < data[0] - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 12; j++)
{
richTextBox2.Text = richTextBox2.
Text + data[i * 12 + j] + "\t";
}
richTextBox2.Text = richTextBox2.
Text + "\n";
}
}
}
}
}
|
